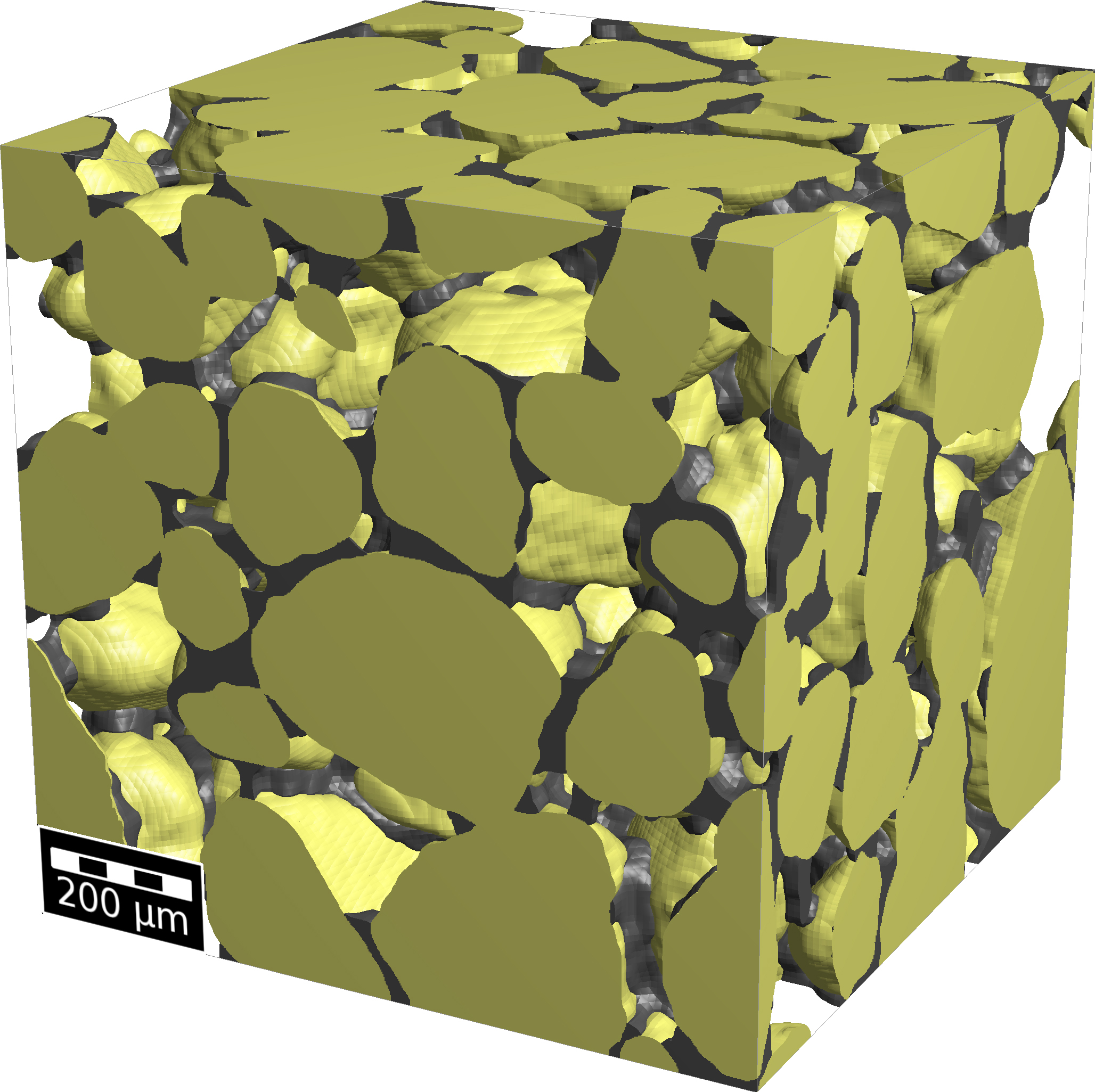
Casting technology uses core sand to map the cooling channels in a cylinder head. Core sand consists of the granular material quartz sand formed to a porous composite by a binder. This is placed in the outer mold before the casting metal and destroyed after the casting process to produce a sand-free casting. We are developing micromechanical simulation models for core sand in cooperation with the Chair of Metal Forming and Casting (UTG) at Technical University of Munich. Starting from input parameters – such as the manufacturing process and the materials used – we calculate effective physical properties like strength, gas permeability and thermal conductivity with GeoDict®.
Calculating the Properties of Inorganically Bound Core Sands
An innovative, inorganic silicate-based binder complies with strict environmental laws and enables sustainable, low-emission production. However, changing the components used changes the physical behavior of the core sand and the result is only visible after passing through the entire process chain. We are able to accelerate development by modeling and simulating the process.