Our well-being in everyday life is strongly influenced by the sounds of our environment. In particular in rooms with bad acoustic properties, sounds grow louder due to theirreflection by smooth, hard surfaces. This reverberance results in a deterioration of articulation. Noise reduction in combination with a simultaneous improvement of articulation helps to decrease noise-induced stress. A respective design of, e. g., the interior acoustics of a car, is an important contribution to driving safety.
Structural Optimization in Mechanics and Acoustics
Modeling
Currently, porous absorbers are used for the improvement of room acoustics. These may consist of different materials, such as:
- glass or mineral wool,
- felts,
- natural or polyester fibers,
- open or closed-cell foams
- fiber reinforced plastics
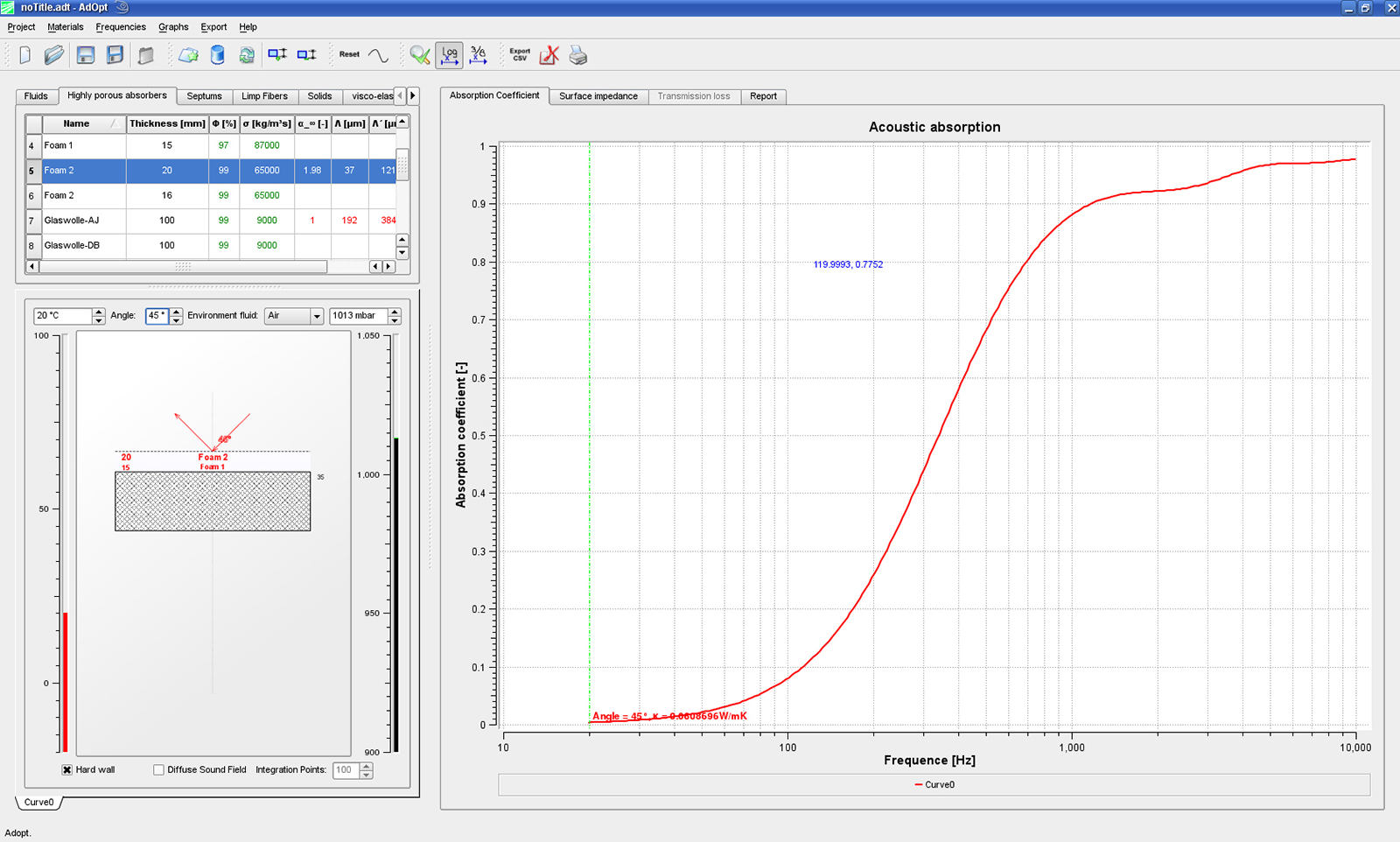
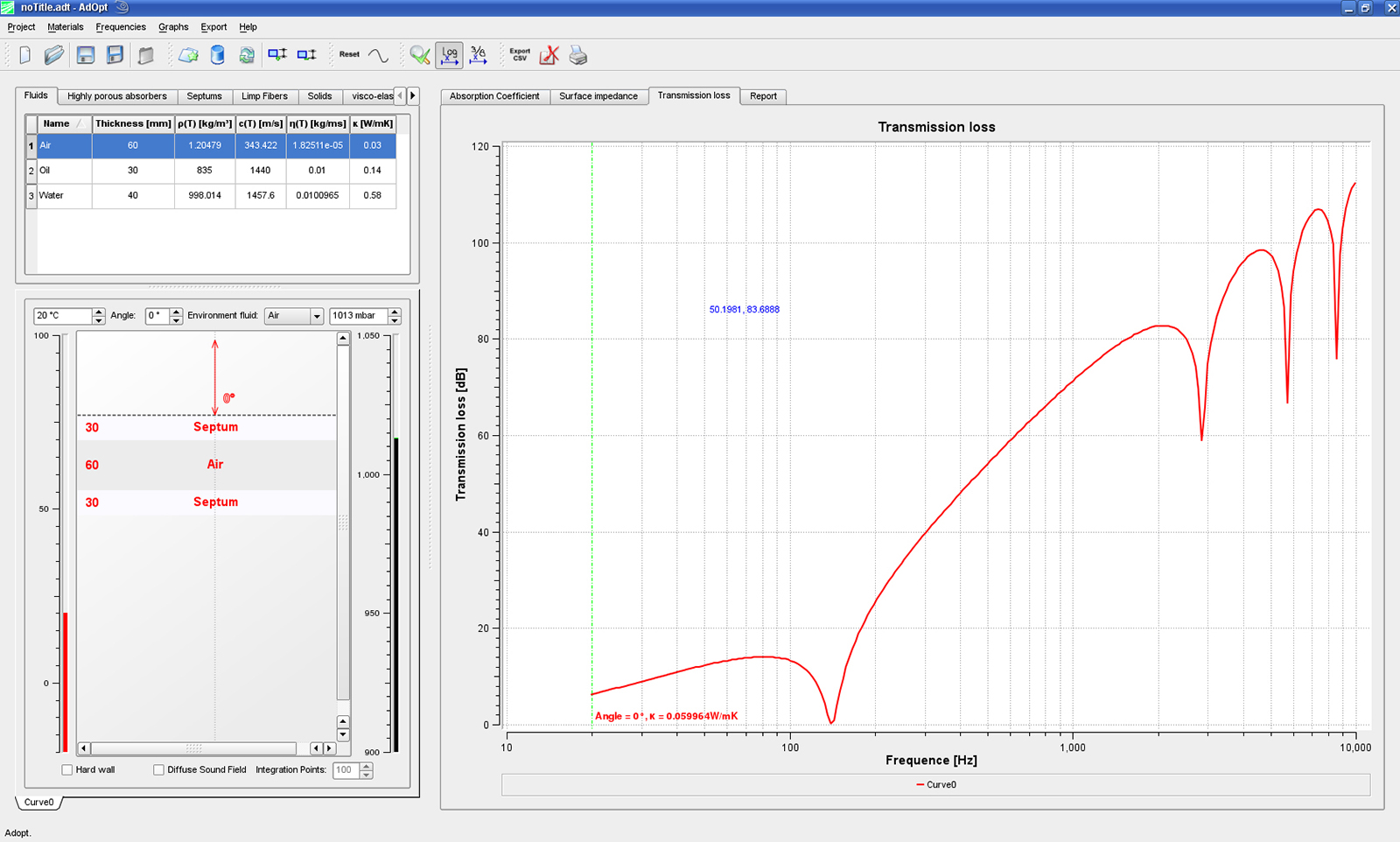
The essential property of porous absorbers is a resistance to the incident sound wave, resulting in a damping effect. From a physical point of view, the damping results from the friction between air molecules and absorber skeleton. Hence, the acoustic absorption can be computed on the basis of a flow problem, where the flow resistance is determined by the solution of the Stokes equation for the complicated microstructure.
The computation of the acoustic properties The computation of the acoustic properties to completely new possibilities of material optimization. First, the measured microstructure is reconstructed by a stochastic model with the software package GeoDict (www.geodict.com), which has been developed at the ITWM. The complicated absorber structure can now be specifically varied on the computer, in order to study the influence of different parameters on the acoustic properties, such as fiber diameter, orientation, or compression.
Transferability
Which influence does a component consisting of the absorber material have on the room acoustics? The answer to this question is provided by a statistical energy analysis (SEA) of the entire system which includes the microscale results as parameters. A large potential for acoustic optimization is provided by so-called layer absorbers. The selection of appropriate material parameters and layer thicknesses allows for an almost arbitrary variation of acoustic properties. Hence, the computer simulations assist the selection of an optimal material.
Another type of porous absorbers are viscoelastic foams. The acoustic behavior of these materials is additionally determined by the mechanical properties of the solid matter. These properties, e. g., the elastic modulus, can also be computed at the ITWM if the microstructure is given.
We Offer
- modeling of acoustic properties of
- porous sound absorbers and layered systems of porous absorbers
- viscoelastic absorbers and layered systems of viscoelastic absorbers
- parameter studies on the basis of stochastic models
- a web-based software tool including:
- data base for the management of acoustic measurement data (individually configurable)
- simulation of acoustic absorbers
- optimization tool for a material selection (desired absorption, material thickness, price, etc.)
- data base for the management of acoustic measurement data (individually configurable)