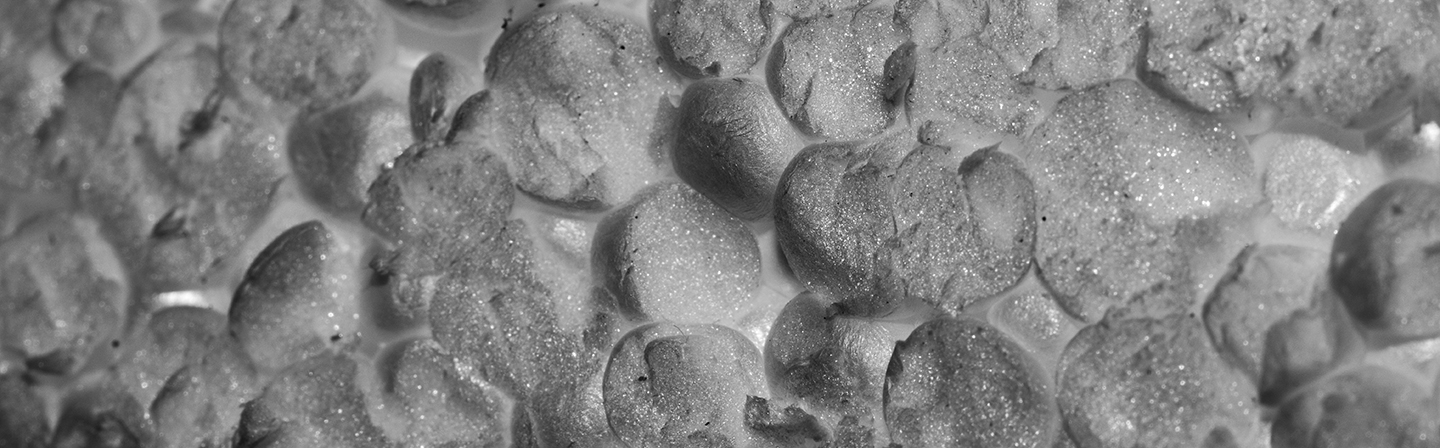
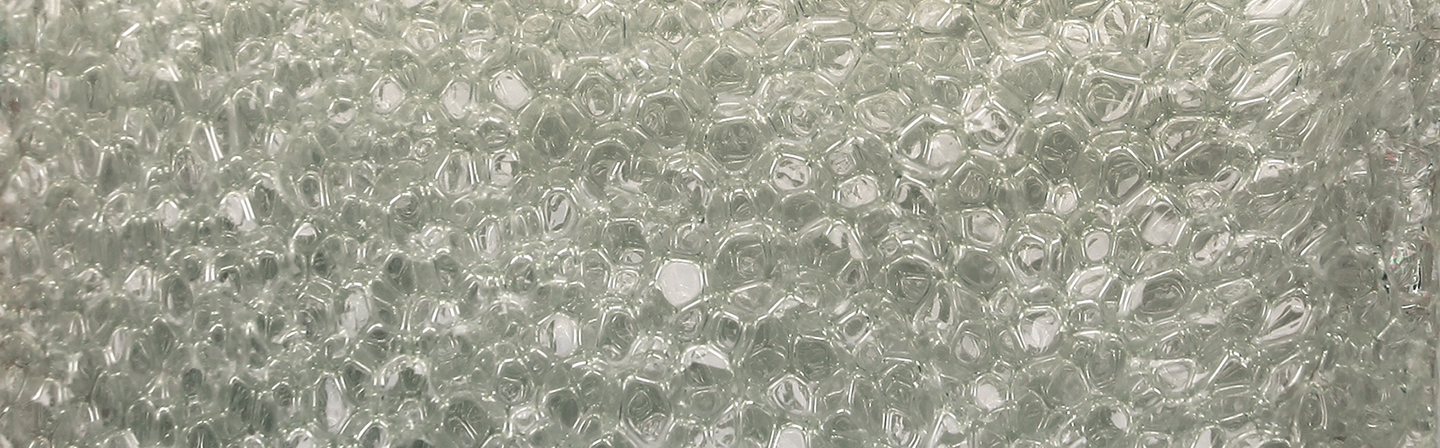
Insulation materials are highly porous fibre structures or foam structures, which should exhibit as low as possible heat conductivity on the one hand, but on the other hand they have to be permanently stable, too.
These are, for example, the following materials:
- Metal / plastic foams
- Fiber insulation materials (e.g., glass / stone wool or natural fiber)
- Cellulose insulation materials
The ideal choice of material structure demands the determination of the different material properties and the quantitative validation of the conflicting criteria. The part of mathematics dealing with effective material properties of porous media is the theory of homogenization. The effective material properties are computed as solutions of ''cell-problems'', which are formulated on representative elementary volumes.