Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles Benefits from the Methods
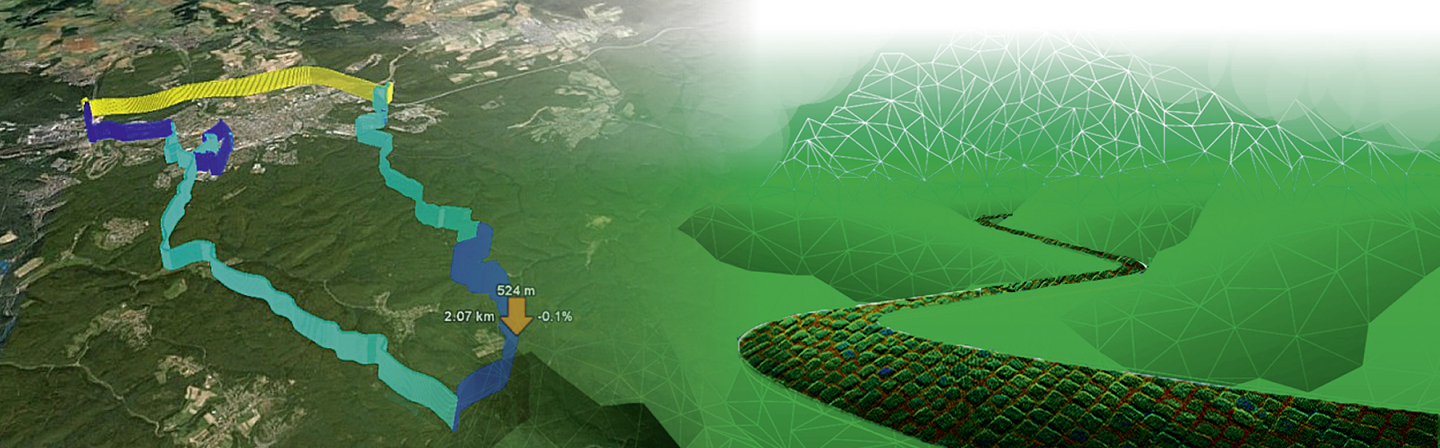
That process was, among others, executed in a common project with Volkswagen Nutzfahrzeuge and reported during the VDI conference Commercial Vehicles 2015 in Eindhoven. Some of the applied methods, e.g. extending the evaluation of measured data using geo-referenced information and the statistical analysis based on factor models, we have been presented in more detail during the DVM-conference of the AK Betriebsfestigkeit 2016 in Steyr.
Prove Reliability
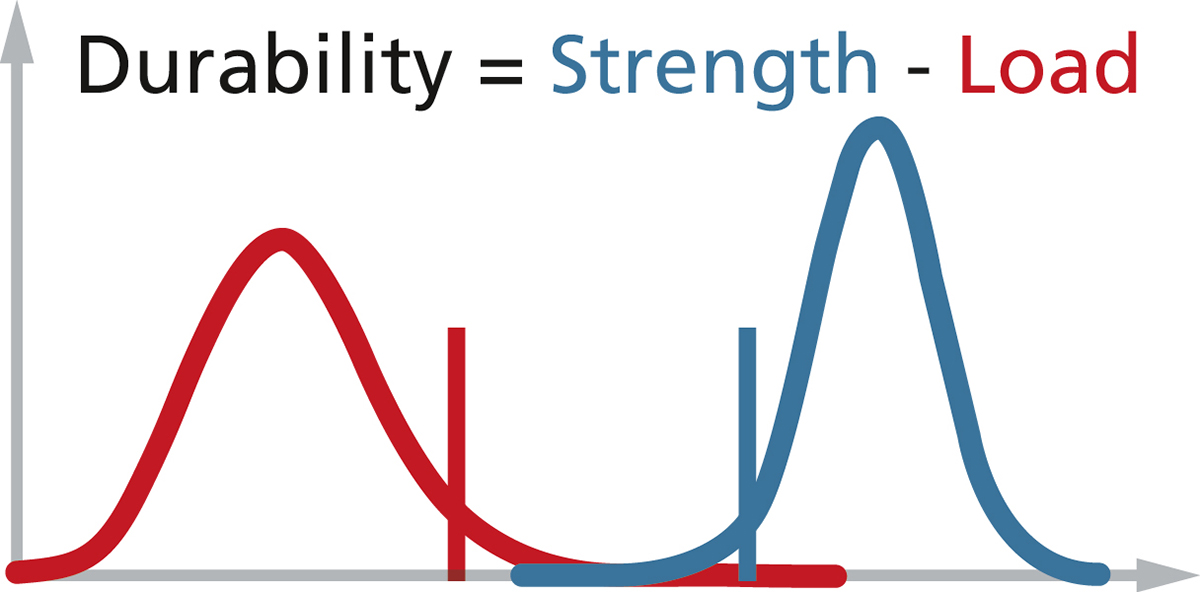
For demonstrating the required reliability of a component based on release tests, safety factors are introduced to cope with the remaining uncertainty due to lack of knowledge in the extreme tails of the load and strength distributions. In addition, statistical reasoning is needed for estimating how many specimens have to be tested in order to prove a certain reliability with a certain confidence.
Finally, we evaluate the reliability tests using statistically validated methods. This applies to comparatively simple component tests as well as to very expensive and long-running complete vehicle tests. The optimal planning of such tests is a decisive point.
- Are many short tests or very few longer tests better suited?
- How can you get the maximum amount and quality of information and benefit from a few tests?
We develop and apply methods for supporting the sketched process with focus on the vehicle industry including construction and agricultural machinery. However, other applications such as wind turbines or railway industry are also covered. Most of the methods are applicable as well within the assessment of energy efficiency or fuel consumption.