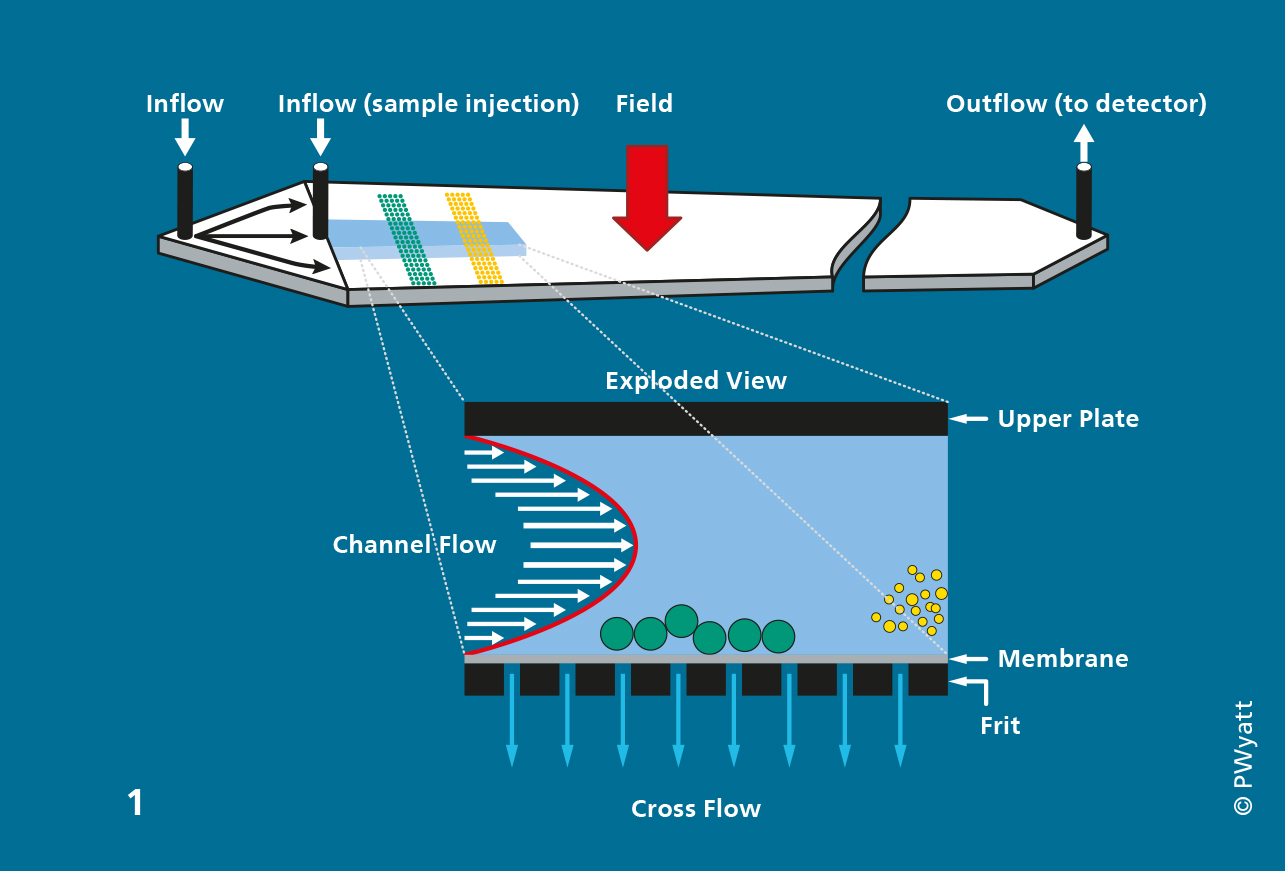
Asymmetrical Flow Field-Flow Fractionation, AFFFF, and Electrical Field-Flow Fractionation, EFFF, are simple, efficient and robust approaches for separation of nano- and micron-size particles in solutions and dispersions. AFFFF technology is well developed and widely used by industry and academia. It exploits the interplay between diffusion and flow filed for particles with different hydrodynamic radii.
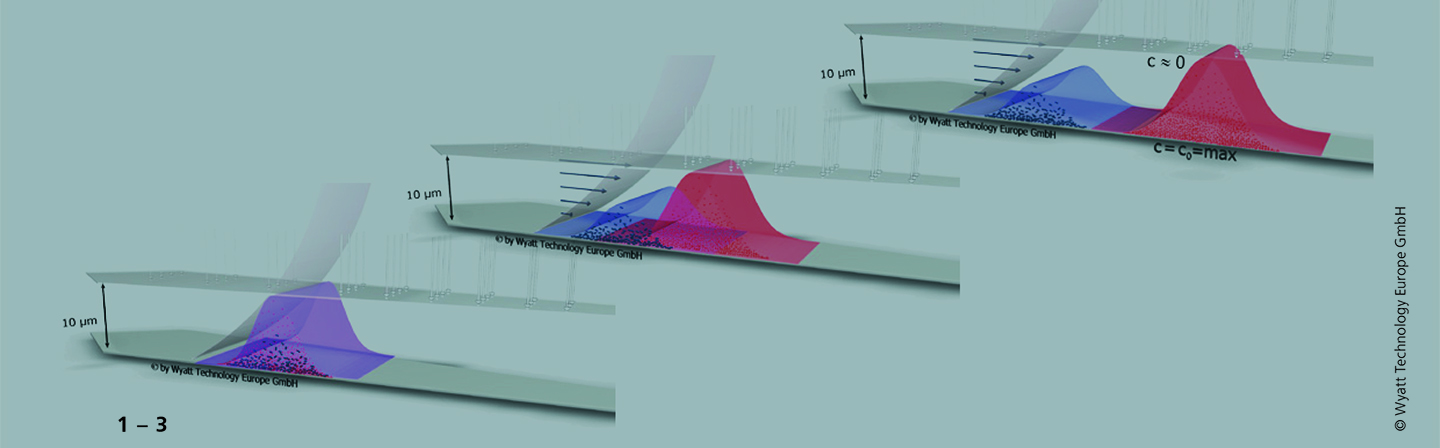
Schematic Representation of the AFFFF Process
The diagram above shows a schematic representation of the AFFFF: Particles having different hydrodynamic radius and thus different diffusion are separated based on the interaction between a horizontal parabolic flow and the interplay between the diffusion and a vertical cross flow.
- Initial stage: The different size particles are mixed, the particle distribution functions overlap.
- The distribution functions for the different size particles start to separate with the time because the smaller particles have larger diffusion coefficient which lifts them in the area of higher horizontal velocity.
- The goal is achieved, when the two types of particles are separated.
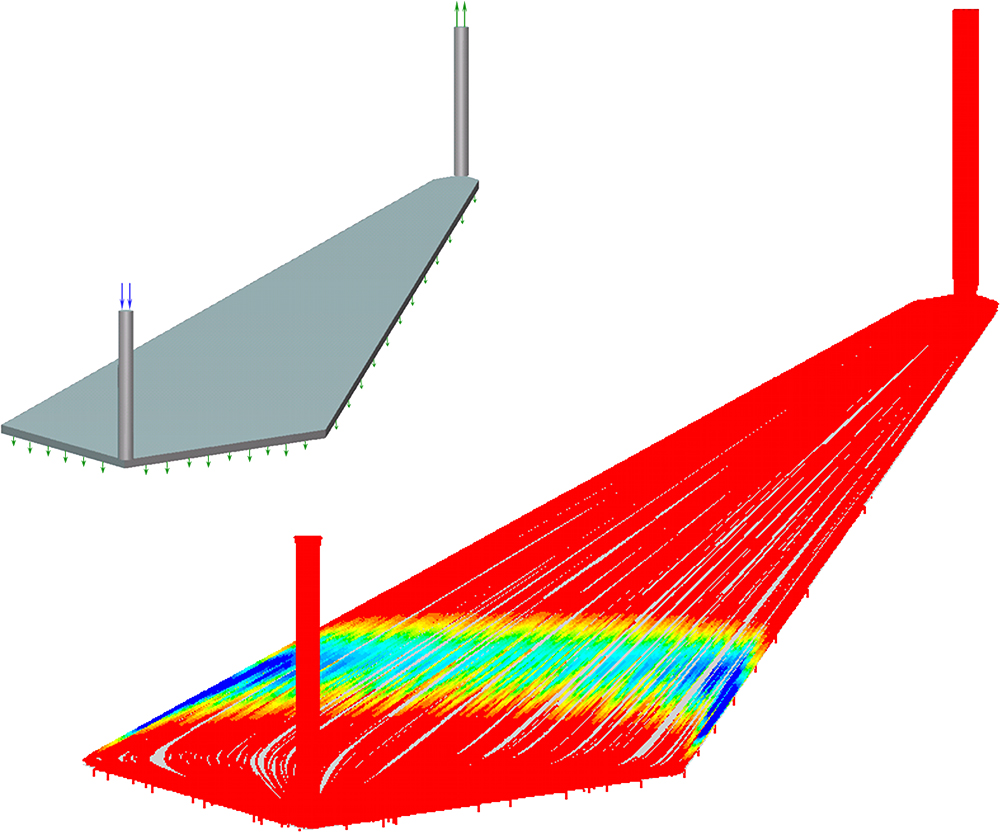
The design of the seperation system is based on a careful analytical study of fluid flow and of separation in a microchannel. Further improvement in the design and the performance of the fractionation devices can be achieved via mathematical modeling and computer simulation.