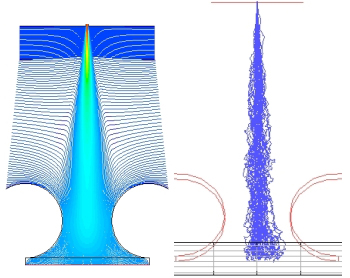
The filament dynamics is determined globally by the direction and strength of the free jet, whereas local evasive movements are essentially resulting from the flow turbulences and their impact on the filaments in combination with the deceleration of the flow above the deposition belt. The randomness of the movement results in the deposition of stochastic structures which are to be optimized with respect to the resulting tensile tenacity of the nonwoven.
Stochastic Deposition Model
The stochastic deposition model is based on the fact that, as observed from above, an individual filament clusters around a center when hitting the belt. The analysis of the respective distribution results in a standard deviation in machine direction (MD) as well as in crosswise direction (CD). Typically, the value for MD is higher than that for CD, which also corresponds to the values for the tenacity. An entire number of approximately 30 different design variations have been developed and evaluated by simulation in order to broaden the filament deposition in CD, simultaneously at least maintaining that in MD.
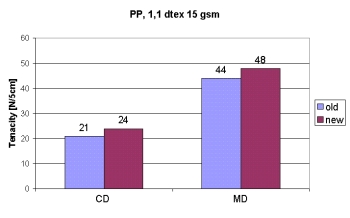
One proposal was selected together with Neumag which promised a significant improvement and could be realized for a plant width of 7 m. The first results after the realization on the plant of the Neumag "Technikum" were presented during the EDANA Symposium 2007. The simulation results were confirmed: the tenacity in crosswise direction (CD) had increased by approximately 15 per cent and by almost 10 per cent in MD, the input of material remaining unaltered.
Type of Project: Industry Project
Project Partner: Oerlikon | Neumag, Neumünster